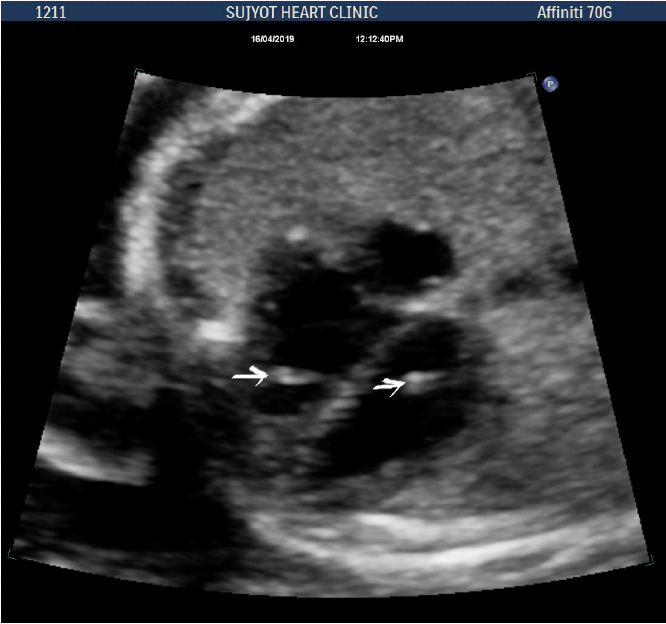
- Not infrequently, serious cardiac defects are confused as echogenic focus in fetal heart.
- Lets understand what is echogenic focus in heart and which cardiac defects one should be careful about.
What is echogenic focus in heart?
- Bright spot seen in heart during evaluation of fetus.
- It disappears by the time of birth or after birth.
- Can be observed 1 in 5 pregnancy, during second and third trimester.
What does it signify?
- In isolation it does not signify any heart defect.
- In isolation, it is not a risk factor for chromosomal anomaly.
- In association with some other anomaly, doctor may ask for genetic evaluation.
How does it look?
- Solitary or multiple
- Involves sub valvar apparatus of tricuspid or mitral valve.
- Not more than 1 or2 mm in dimension.
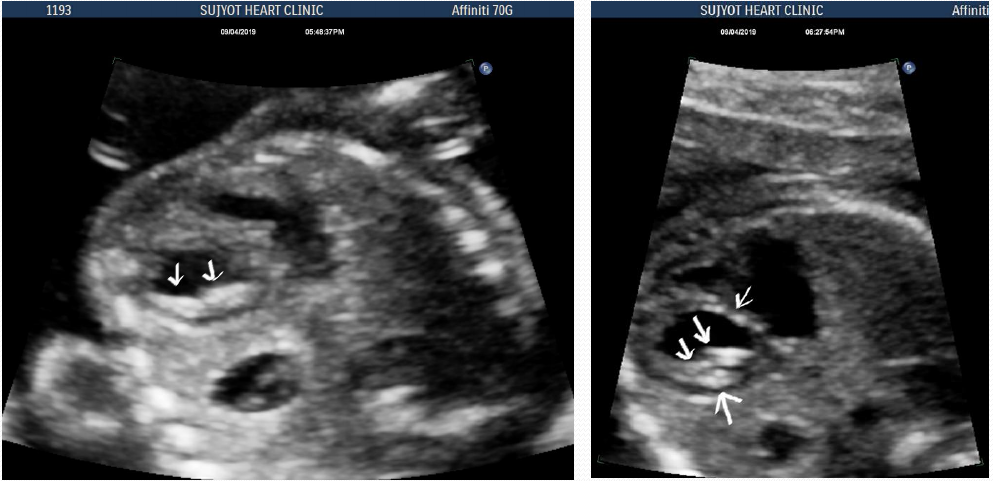
- It most frequently involves left ventricle but can be seen in right ventricle and can be multiple.
Arrows: echogenic foci in LV and RV

Arrow: Multiple echogenic foci in LV and RV
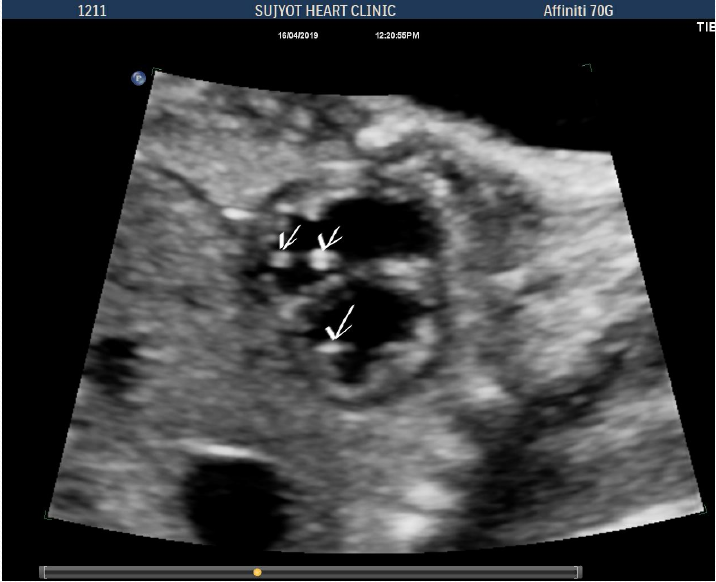
Solitary echogenic focus in heart implies
- Normal LV and RV function and structure
- Normal valves
- Normally related great vessels
Does it need further evaluation?
- Anomaly scan shows defect in any organ
- Maternal risk factors like advance age/ family history / drugs etc
- Fetal risk factors: NT scan, IVF, etc
- In presence of above risk factors, further evaluation is warranted
Other causes of hyper echoic tissue?
- Endocardial fibroelstosis
- Critical aortic stenosis
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrom
- Rhabdomyoma
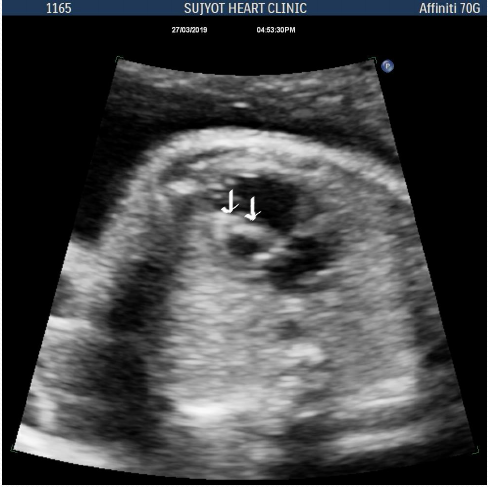
Endocardial fobroelastosis
- Fibrosis of left ventricle endocardium
- Look like hyperechoic tissue involving larger part of LV myocardium, and papillary muscle
- May be associated with HLHS, aortic stenosis or isolated findings
- High chances of fetal demises when diagnosed in utero.
How it does not look?
- Involvement of large part of endocardium
- Abnormal valves, mainly mitral hypoplasia and regurgitation
- Depressed left ventricular function
- Hypoplastic aortic valve
- May have flow reversal in arterial duct and oval foramen.
Endocardial fibro elastosis of LV
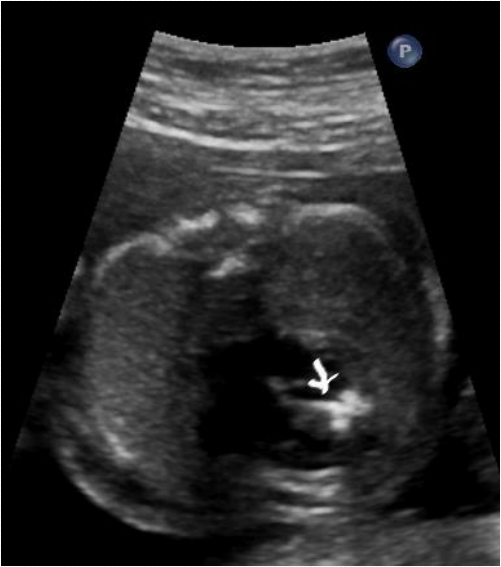
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- Characterized by small left ventricle
- Hypoplasia or atresia of mitral and aortic valve
- May have endocardial fibroelastosis.
- Flow reversal in oval foramen and distal aortic arch
- Aortic stenosis ( difficult to diagnose in utero)
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Small LV and hyper echoic myocardium
Severe aortic stenosis
- Bi cuspid or mono cuspid aortic valve.
- LV may dilate and become dysfunctional
- Extensive endocardial fibroelastosis
- Flow reversal in distal aortic arch may be present
- May develop into hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Hyper echoic LV endocardium in aortic stenosis
Endocardial fibroelastosis and dilated dysfuntional LV
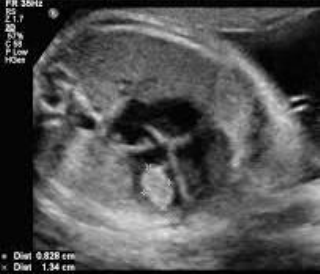
Rhabdomyoma
- Associated with tuberous sclerosis
- Affects mainly ventricle
- Single or multiple
- May cause obstruction to mitral/ tricuspid/ aortic or pulmonary valve.
- May regress over time.
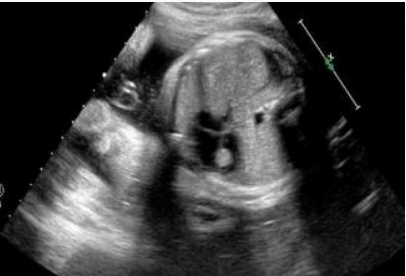
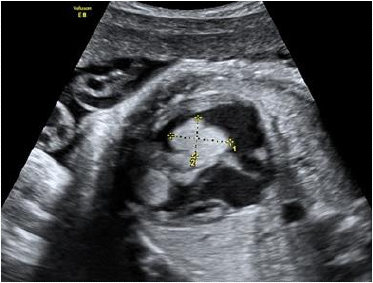
How to deal with echogenic focus in heart?
- Isolated findings may not need further evaluation.
- However; other major cardiac defects can be mis-diagnosed as echogenic focus.
- It remains a diagnosis of exclusion.

REPLY COMMENT